Difference between revisions of "Site-specific workpiece activation"
(→Related: added * Spectrum of means of assembly) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Stub}} | {{Stub}} | ||
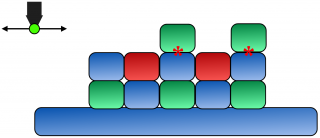
| − | + | [[File:SiteSpecificWorkpieceActivationConcept.png|320px|thumb|right|(1) position XY, (2) acivate Z (makes red *), (3) repeat for all positions where green parts are desired in this this layer (4), wash in the green parts (5) repeat for parts with other colors (6) next layer. Image author: Eric K. Drexler]] | |
Instead of picking up stuff and then placing it to assemble something <br> | Instead of picking up stuff and then placing it to assemble something <br> | ||
site-specific workpiece activation works such that on the surface of a workpiece some spots are activated and then the <br> | site-specific workpiece activation works such that on the surface of a workpiece some spots are activated and then the <br> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* [[Spectrum of means of assembly]] | * [[Spectrum of means of assembly]] | ||
| + | * [[Patterned layer epitaxy]] | ||
* [[Foldamer printer]] | * [[Foldamer printer]] | ||
* [[The various forms of mechanosynthesis]] | * [[The various forms of mechanosynthesis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:46, 5 June 2021
Instead of picking up stuff and then placing it to assemble something
site-specific workpiece activation works such that on the surface of a workpiece some spots are activated and then the
pieces that are meant to be placed on these now activated sites are washed in with some solvent gas (or other means).
"Activation" may mean different things in different instances.
There are at least two example cases for this.
One on the smallest physically scale and one on a bigger scale.
Bigger scale site-pecific workpiece activation
This is present as part of the proposed foldamer printer.
PALE patterned layer epitaxy (experimentally demonstrated)
The near atomically sharp needle tip of a scanning probe is used to abstract hydrogen from a silicon surface in an
positionally atomically precise way.
Subsequently silicon is deposited via gas phase.
Used scanning probes where all macroscopic and big (till before 2021)
miniaturization of scanning probes could speed up the process quite a bit.
This manufacturing method is related to the direct path.