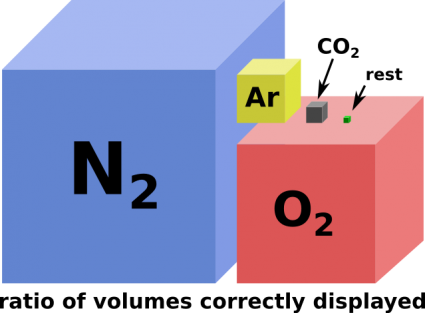
Argon
Argon is a noble gas that is highly abundant in Earths atmosphere.
All other noble gasses (Helium, Neon, –, Krypton, Xenon) are quite rare on Earth.
As a noble gas it does not form bonds to other atoms when uncharged.
It can only be enclosed or held by giving it a charge.
Early (now outdated) concepts of molecular assemblers sometimes came with the proposition
to fill the mechanosynthesis chamber with a noble gas like Helium, Neon, or Argon to inflate a graphene chamber or such.
Especially with the (least reactive) lighter noble gasses this should not bother the process of piezochemical mechanosynthesis.
With atomic number 18 and atomic mass 40 40Ar (99.604%)
it is quite a bit heavier than di-nitronen (atomic mass 14)*2 = 28 despite being monoatomic.
It's thus not usable as a lifting gas.
Stable isotopes:
- 36Ar (0.334%) – #protons = #neutrons
- 38Ar (0.063%)
- 40Ar (99.604%)
Argon condenses and freezes a bit before nitrogen does:
- Melting point 83.81 K
- Boiling point 87.302 K