Difference between revisions of "Assembly levels"
(→Preprocessing (PS=2, AL=0) (prepatation of tooltips): added a note on irreversibility) |
m (→Related) |
||
| (53 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
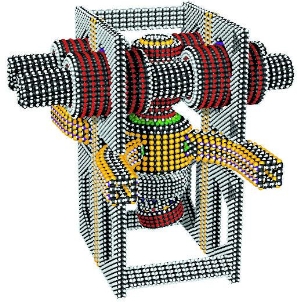
| − | The '''assembly levels''' describe how an advanced productive nanosystem of [[technology level III]] | + | [[File:NanosystemsNotAProposedDesignConvergentAssembly.jpg|350px|thumb|right|'''THIS IS NOT A PROPOSED DESIGN (so explicitly stated in [[Nanosystems]])'''. Just an example of a non-planar [[convergent assembly]] topology and geometry (or morphology as in biology). '''More or less planar [[assembly layers]] likely match natural scaling laws much better.''' {{wikitodo|Add Josh Halls analytic math comparison to scaling laws in bio-systems too. Plus his picture.}}]] |
| + | |||
| + | There are two options how things can be assembled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * in place right from its most fundamental constituents to its final complete form | ||
| + | * out of place from smaller subcomponents to bigger subcomponents in a series of successively bigger assembly stations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The assembly stations plus everything additionally necessary on the same size scale for integrating them into an integrated system like a [[gem-gum factory]] are here defined to be called "assembly levels". | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: Assembly levels do not talk about specific system geometries like e.g. [[assembly lavers]] talk about a layered configuration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Old introduction = | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''assembly levels''' describe how the [[assembly subsystem]] of an advanced productive nanosystem of [[technology level III]] eventually could be organized. <br> | ||
| + | The '''assembly levels''' constitute a greatly implementation agnostic scheme for the organisation of an advanced productive nanosystem on the bottommost levels. <br> | ||
Assembly levels can be e.g. concretely mapped into a [[Nanofactory layers|layered Nanofactory design]] or a partially fractal design. | Assembly levels can be e.g. concretely mapped into a [[Nanofactory layers|layered Nanofactory design]] or a partially fractal design. | ||
| − | Since waste | + | Since non-degradable [[waste]] may be a quite underestimated [[dangers|danger]] of this otherwise potentially extremely clean technology a special focus on [[recycling]] is taken here. |
| − | + | * A concrete implementation of the lower assembly levels is shown in the concept visualization video [[Productive Nanosystems From molecules to superproducts]]. | |
| + | * Assembly levels may aid in the [[design of gem-gum on-chip factories]] | ||
* Do not confuse ''[[convergent assembly]]'' with ''[[self replication|exponential assembly]]''. | * Do not confuse ''[[convergent assembly]]'' with ''[[self replication|exponential assembly]]''. | ||
| − | |||
* The here used ''terms in italic'' are newly proposed. | * The here used ''terms in italic'' are newly proposed. | ||
| − | |||
= A Listing of Levels = | = A Listing of Levels = | ||
| − | + | * PS … processing step (or PL processing level) | |
| + | Subclassification of PS: | ||
| + | * PPS … preprocessing step (or PPL preprocessing level) | ||
| + | * AL … assembly level in the stage of assembly levels (encompassing both mills stage and manipulators stage) | ||
| + | Subclassification of ALs: | ||
| + | * MiL … Mill level in the stage of all mill levels | ||
| + | * MaL … Manipulator Level in the stage of all manipulator levels | ||
| − | + | == Take-in and preprocessing == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | At the very first two processing steps |
| − | * | + | * there is no real constructive assembly yet |
| + | * the manipulated structures do not yet grow in size | ||
| + | Given the absence of assembly these two processing steps will be not included in the assembly levels. | ||
| − | + | === Preprocessing step 1 – Take-in of resource molecules === | |
| − | + | * Resource material gets filtered/cleaned. Contaminants are removed. <br> | |
| + | * Liquid phase (and maybe gas phase) processing is involved here. <br> | ||
| + | * Significant heat can be generated from moving to [[machine phase]]. This energy is potentially recuperable. | ||
| − | + | For more details see main page: [[Preprocessing step 1 (gem-gum factory)]] <br> | |
| − | + | Also see: [[Purification mills]], [[Acetylene molecule sorting pump]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === Preprocessing | + | === Preprocessing step 2 – preparation of tooltips === |
| − | + | * Discharged [[tooltip]]s get reloaded and with [[resource molecules]] from pockets of the former processing step | |
| + | * This step and all follwing ones happen in [[machine phase]] only. | ||
| + | * Tip bound [[resource molecules]] get their bonds ripped open. <br>They become activated highly reacive moieties / molecule fragments | ||
| + | * Recharged [[tooltip]]s get delivered to the next processing step which is the first assembly level. | ||
| − | + | For details see main page: [[Preprocessing step 2 (gem-gum factory)]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == First assembly level – (''from molecule fragments to crystolecules'') == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* '''In goes:''' fully preprocessed [[moieties]] on reusable tools | * '''In goes:''' fully preprocessed [[moieties]] on reusable tools | ||
* '''Out goes:''' assembled [[crystolecule]]s | * '''Out goes:''' assembled [[crystolecule]]s | ||
| − | * | + | * '''Where processing is done:''' [[robotic mechanosyntesis core]]s in specialized assembly lines. |
| − | * | + | * '''What processing is done:''' [[force applying mechanosynthesis]] in [[molecular mills]] <br>very stiff bulky design of mill wheels and assembly lines – hard-coded operation |
| − | + | * This is the third processing step after the the two preprocessing steps. | |
| + | * This is the first real assembly level where small parts are getting put together to much bigger parts. | ||
| − | + | For details see main page: [[Assembly level 1 (gem-gum factory)]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Second assembly level (''from crystolecules to crystolecular units'') == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * '''In goes:''' fully mechanosyntheized [[crystolecule]]s without or with some bonds intentionally left open (including [[crystolecule fragments]]) | |
| − | + | * '''Out goes:''' assembled [[crystolecular unit]]s (including bigger [[Diamondoid crystolecular machine element]]) | |
| − | + | * '''Where processing is done:''' [[crystolecule to crystolecular unit assembly chamber]]s. Possibly mill style. | |
| − | + | * '''What processing is done:''' Pick and place assembly with various adapters for basic end-effectors. <br>Assembly including more or less of [[covalent welding]] depending on the nature of the product under construction.<br> | |
| − | + | For details see main page: [[Assembly level 2 (gem-gum factory)]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == Third assembly level: (''from crystolecular units to microcomponents'') == |
| − | + | * '''In go:''' fully assembled [[crystolecular unit]]s | |
| − | + | * '''Out go:''' assembled [[microcomponent]]s | |
| − | + | * '''Where processing is done:''' [[Level 3 assembly chamber]]s. | |
| − | + | * '''What processing is done:''' Pick and place assembly (with some adapters for basic end-effectors | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | For details see main page: [[Assembly level 3 (gem-gum factory)]] | |
| − | + | == Fourth assembly level – (''from microcomponents to product fragments'') == | |
| − | + | '''Main page: [[From microcomponent to mesocomponent assembly level]]''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | Summarized characteristics of this assembly level: |
| + | * '''In goes:''' fully assembled [[microcomponents]] | ||
| + | * '''Out goes:''' assembled [[product fragment]]s – (or the final product right away) | ||
| + | * '''Where processing is done:''' robotic assembly chambers (clean room) | ||
| + | * '''What processing is done:''' Pick and place assembly with just a few if any adapters for the end-effectors. <br> Much more filigree robotics here since stiffness is no longer so critical. Eventual part streaming robotics here. | ||
| − | + | First assembly level supporting fully reversible assembly! | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | For details see: [[Assembly level 4 (gem-gum factory)]] | |
| − | + | == Fifth assembly level – Level V == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | |
An optional step. Some layers of [http://e-drexler.com/p/04/04/0507molManConvergent.html convergent assembly] can be added fro various reasons. | An optional step. Some layers of [http://e-drexler.com/p/04/04/0507molManConvergent.html convergent assembly] can be added fro various reasons. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 115: | ||
'''Recycling:''' A level IIIb and IIb system may be included into the product that bypasses Level IV so that products can execute self repair actions while running. (hot plugging) | '''Recycling:''' A level IIIb and IIb system may be included into the product that bypasses Level IV so that products can execute self repair actions while running. (hot plugging) | ||
| − | =Related topics= | + | = Related topics = |
== Interleaved component router systems and stocks == | == Interleaved component router systems and stocks == | ||
| Line 188: | Line 154: | ||
= Related = | = Related = | ||
| − | * [[Convergent assembly]] | + | * '''[[Gemstone metamaterial on chip factory]]''' |
| + | * '''[[Assembly layers]]''' | ||
| + | * '''[[Convergent assembly]]''' | ||
* [[In place assembly]] | * [[In place assembly]] | ||
* More general including the in between levels (not necessarily layers): [[Chain of zones]] | * More general including the in between levels (not necessarily layers): [[Chain of zones]] | ||
| + | * [[Tracing trajectories of component in machine phase]] | ||
| + | * [[Assembly level crossover (gem-gum factory)]] | ||
| + | * [[Productive Nanosystems From molecules to superproducts]] | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | * [[Selfassembly level]] | ||
= External links = | = External links = | ||
| Line 201: | Line 174: | ||
{{Assembly levels}} | {{Assembly levels}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:PagesWithNiceTables]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:03, 1 March 2024
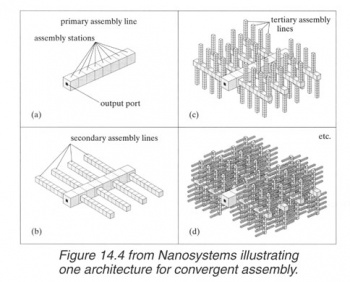
There are two options how things can be assembled.
- in place right from its most fundamental constituents to its final complete form
- out of place from smaller subcomponents to bigger subcomponents in a series of successively bigger assembly stations.
The assembly stations plus everything additionally necessary on the same size scale for integrating them into an integrated system like a gem-gum factory are here defined to be called "assembly levels".
Note: Assembly levels do not talk about specific system geometries like e.g. assembly lavers talk about a layered configuration.
Contents
- 1 Old introduction
- 2 A Listing of Levels
- 2.1 Take-in and preprocessing
- 2.2 First assembly level – (from molecule fragments to crystolecules)
- 2.3 Second assembly level (from crystolecules to crystolecular units)
- 2.4 Third assembly level: (from crystolecular units to microcomponents)
- 2.5 Fourth assembly level – (from microcomponents to product fragments)
- 2.6 Fifth assembly level – Level V
- 3 Related topics
- 4 Related
- 5 External links
Old introduction
The assembly levels describe how the assembly subsystem of an advanced productive nanosystem of technology level III eventually could be organized.
The assembly levels constitute a greatly implementation agnostic scheme for the organisation of an advanced productive nanosystem on the bottommost levels.
Assembly levels can be e.g. concretely mapped into a layered Nanofactory design or a partially fractal design.
Since non-degradable waste may be a quite underestimated danger of this otherwise potentially extremely clean technology a special focus on recycling is taken here.
- A concrete implementation of the lower assembly levels is shown in the concept visualization video Productive Nanosystems From molecules to superproducts.
- Assembly levels may aid in the design of gem-gum on-chip factories
- Do not confuse convergent assembly with exponential assembly.
- The here used terms in italic are newly proposed.
A Listing of Levels
- PS … processing step (or PL processing level)
Subclassification of PS:
- PPS … preprocessing step (or PPL preprocessing level)
- AL … assembly level in the stage of assembly levels (encompassing both mills stage and manipulators stage)
Subclassification of ALs:
- MiL … Mill level in the stage of all mill levels
- MaL … Manipulator Level in the stage of all manipulator levels
Take-in and preprocessing
At the very first two processing steps
- there is no real constructive assembly yet
- the manipulated structures do not yet grow in size
Given the absence of assembly these two processing steps will be not included in the assembly levels.
Preprocessing step 1 – Take-in of resource molecules
- Resource material gets filtered/cleaned. Contaminants are removed.
- Liquid phase (and maybe gas phase) processing is involved here.
- Significant heat can be generated from moving to machine phase. This energy is potentially recuperable.
For more details see main page: Preprocessing step 1 (gem-gum factory)
Also see: Purification mills, Acetylene molecule sorting pump
Preprocessing step 2 – preparation of tooltips
- Discharged tooltips get reloaded and with resource molecules from pockets of the former processing step
- This step and all follwing ones happen in machine phase only.
- Tip bound resource molecules get their bonds ripped open.
They become activated highly reacive moieties / molecule fragments - Recharged tooltips get delivered to the next processing step which is the first assembly level.
For details see main page: Preprocessing step 2 (gem-gum factory)
First assembly level – (from molecule fragments to crystolecules)
- In goes: fully preprocessed moieties on reusable tools
- Out goes: assembled crystolecules
- Where processing is done: robotic mechanosyntesis cores in specialized assembly lines.
- What processing is done: force applying mechanosynthesis in molecular mills
very stiff bulky design of mill wheels and assembly lines – hard-coded operation
- This is the third processing step after the the two preprocessing steps.
- This is the first real assembly level where small parts are getting put together to much bigger parts.
For details see main page: Assembly level 1 (gem-gum factory)
Second assembly level (from crystolecules to crystolecular units)
- In goes: fully mechanosyntheized crystolecules without or with some bonds intentionally left open (including crystolecule fragments)
- Out goes: assembled crystolecular units (including bigger Diamondoid crystolecular machine element)
- Where processing is done: crystolecule to crystolecular unit assembly chambers. Possibly mill style.
- What processing is done: Pick and place assembly with various adapters for basic end-effectors.
Assembly including more or less of covalent welding depending on the nature of the product under construction.
For details see main page: Assembly level 2 (gem-gum factory)
Third assembly level: (from crystolecular units to microcomponents)
- In go: fully assembled crystolecular units
- Out go: assembled microcomponents
- Where processing is done: Level 3 assembly chambers.
- What processing is done: Pick and place assembly (with some adapters for basic end-effectors
For details see main page: Assembly level 3 (gem-gum factory)
Fourth assembly level – (from microcomponents to product fragments)
Main page: From microcomponent to mesocomponent assembly level
Summarized characteristics of this assembly level:
- In goes: fully assembled microcomponents
- Out goes: assembled product fragments – (or the final product right away)
- Where processing is done: robotic assembly chambers (clean room)
- What processing is done: Pick and place assembly with just a few if any adapters for the end-effectors.
Much more filigree robotics here since stiffness is no longer so critical. Eventual part streaming robotics here.
First assembly level supporting fully reversible assembly!
For details see: Assembly level 4 (gem-gum factory)
Fifth assembly level – Level V
An optional step. Some layers of convergent assembly can be added fro various reasons. One can think of convergent assambly as putting microcomponents together from the leaves to the root of an octree.
Todo: Find out the advantages of convergent assembly over direct assembly. (It's not speed.) They are mentioned but not really explained here: [1] Exponential assembly is more sensitive to disturbing vibrations / accelerations than direct assembly. Proucts are more anisotropic. A lot of quick macroscopic handling (makro scale reconfigurations) may be automated in a convergent assembly nanofactory capable of dealing with dirt from recycling. Interfaces / surfaces capable of self alignment and bonding from crude alignment by hand (quasi welding) would allow the topmost convergent assembly stages huge fault tolerances.
Recycling: A level IIIb and IIb system may be included into the product that bypasses Level IV so that products can execute self repair actions while running. (hot plugging)
Related topics
Interleaved component router systems and stocks
For the transport of unfinished product parts of different sizes from lower to higher assembly levels nanofactories may use routing structures.
The routing structures can either have separate or merged multiplexing and de-multiplexing steps where the former provides redundancy of rails. (Nanosystems Fig 14.7.)
There are two in some respects similar yet in other respects very different steps where this can occur.
- when diamondoid molecular elements (DMEs) are transported from assembly level I to II
- when microcomponents are transported from assembly level II to III
For all the optional steps in convergent assembly (assembly level IV) the lower stages should be programmable/steerable enough that no further shuffling is required. (Depending on the programmability the lower stages may too be simplified.)
Since direct control of the bottommost systems could clog the IO bottleneck hirachical heterogenous nanomechanical computing system must be integrated in parallel (one layer might suffice). Temporary storage facilities for microcomponents are optional (they may also be useful as seperate macroscopic entities).
[Todo: explain free space designs, analyze parallelism]
Product expulsion
In any technology level III productive nanosystem that uses vacuum up to the topmost assembly level (blending assembly levels, allowing for unrecyclable macroscopic maximum performance single crystals) a macroscopic perfectly tight lockout mechanism is necessary.
Vacuum lockout in the micro-scale at the soonest possible point in the convergent assembly process like described here may be easier and may enforce recyclability of products at the price that one needs to deal with dirt not just in product usage but already at the assembly time.
In E.Drexlers new book "Radical Abuncance" [add ref] the outlined system differs to the presented assembly levels in that it keeps the process in vacuum/noble-gas till the product is completely finished. This design avoids the complexity of dealing with dirt but introduces the complicity of providing appropriate vacuum at all convergent assembly levels (level IV). Note that for recycling one has to deal with dirt at least on the products surface in any way. An "isolation till finished macro-product" approach would further allow intermixing for Level II & III and thus allow for undissasemblable unrecyclable macro-products like one big diamond crystal. Such products may only be of interest for products that not just ought to work but are supposed to push the limits like in motor sports and in military interests. Well designed form closure connectors can retain almost the full material strength and may suffice for aerospace applications.
Recycling
A very important issue whenever responsibly designing nanomachinery is to aim for best waste avoidance. It does not come for free. The history of plastics show the dangers pretty well. But with APM systems one can take a range of countermeasures starting in their inherent design and buildng up with additional functions. Very desirable would be some kind of global microcomponent redistribution system parallel to our current water gas and electricity supply that couples to assembly level IIb.
Relation to product structure
Somewhat complementary to the assembly levels is hirachical product structure. A given product description (e.g. implicit volume definition) can be reversely subdivided into assembly level assembly steps and the assembly levels can be used as a guide for foreward product design (which is most prominent with microcomponents). [TODO: link Nanosystems]
Related
- Gemstone metamaterial on chip factory
- Assembly layers
- Convergent assembly
- In place assembly
- More general including the in between levels (not necessarily layers): Chain of zones
- Tracing trajectories of component in machine phase
- Assembly level crossover (gem-gum factory)
- Productive Nanosystems From molecules to superproducts
External links
- Motivations for splitup into assembly levels (Level1 & Level2) can be found in Considerations for Self-replicating Manufacturing Systems by J. Storrs Hall, PhD. Institute for Molecular Manufacturing [2] [3]
Table of assembly levels
| How products are put together | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building block | Assembly step | |||
|
|
Level 0a: (~size<1nm) capturing sorting and purifying resource molecules from gas phase water or organic solution | |||
|
Level 0b: (~size~1nm) from captured raw material Molecules (above) to Moieties on tooltips (left) | |||
|
Level I: (~size<32nm) from Moieties on tooltips (above) to crystolecules (left) | |||
|
Level IIa: (~size~32nm) from crystolecules (above) to more or less monolithic parts (left) | |||
[todo: add other examples]
|
Level IIa: (~size~<1µm) from more or less monolithic parts (above) to recomposable µ-components (left) | |||
|
|
Level III: (~size~<32µm) from recomposable µ-components above to µ-component assemblies (left) | |||
|
|
Level III or higher: (~size>32µm) from µ-component assemblies (above) to diamondoid metamaterials (left) |
|||
|
|
Level III or higher: (~size>>32µm) from metamaterials (above) to yet alien products (left) | |||